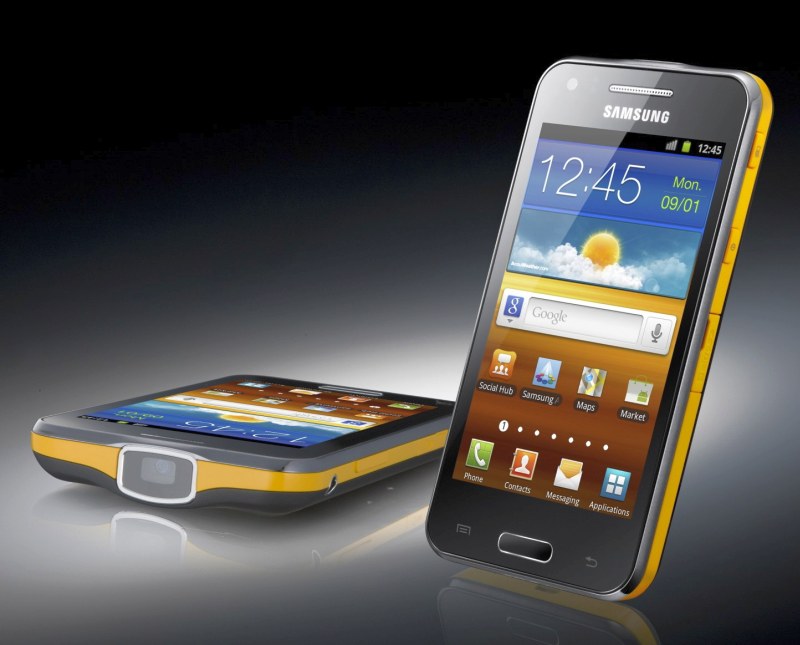
Samsung has announced its updated projector phone dubbed the ‘Galaxy Beam’. The Beam comes with Android 2.3 and a 1GHz dual-core CPU, and is equipped with an integrated projector of 15 lumen brightness. The Beam also has 4-inch WVGA screen 8GB of onboard storage and 768 MB of RAM , along with a 2000 mAh battery to keep it going. The Galaxy Beam can supposedly rock a 50 inch wide projection in a nice low light environment.
For connectivity you have BT 3.0?HS, Wifi 802.11 b/g/n 2.4GHz, camera is a 5MP AF ? 1.3MP and Flash at back. Of course Samsung has customized the UI with their very own TouchWiz. The full specs are in the PR below.
[toggle title_open=”Press Release” title_closed=”Press Release” hide=”yes” border=”yes” style=”default” excerpt_length=”0″ read_more_text=”Read More” read_less_text=”Read Less” include_excerpt_html=”no”]
Share the Fun with Samsung GALAXY Beam
February 26, 2012
Samsung’s projector smartphone offers unforgettable shared experience for playing multimedia content anytime, anywhere
Barcelona – February 26, 2012 – Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd, a global leader in digital media and digital convergence technologies, today introduced Samsung GALAXY Beam, the projector smartphone that allows users to display and share multimedia content anywhere on a large luminous projector screen.
GALAXY Beam lets users spontaneously share photos, videos or other digital media with family or friends by beaming content stored on the device directly onto walls, ceilings or improvised flat surfaces, so that everyone can share the fun without the need to huddle around smartphone or pad-sized screens. GALAXY Beam’s ultra-bright 15 lumens projector allows users to freely share life’s memorable moments instantly and in crisp clarity, even in outdoor environments.
“GALAXY Beam provides mobile freedom, enabling a unique shared experience around digital content for everyone-anywhere and instantly-from a smartphone as slim and portable as any on the market,” said JK Shin, President of IT & Mobile Communications Division at Samsung Electronics.
GALAXY Beam is a device borne out of Samsung’s insight and innovation, demonstrating Samsung’s commitment to providing extraordinary experiences for consumers with products that let them express and fulfill themselves.”
Video clips, maps, business information, games – a whole range of multimedia content can be beamed instantly by GALAXY Beam on a crisp, high-definition projection up to 50” wide. The device features a projector-dedicated application which makes it easy to select content and activate projection in a few simple steps.
Add a dose of ambience or entertainment to a friends’ gathering by transforming any household room or outdoor deck into an instant mini home-theater, projecting full-screen video clips on a ceiling or wall for common sharing, at the touch of a button. Or capture your favorite holiday moments using the GALAXY Beam’s 5MP camera, then display a full photo slideshow to family members on a dining room wall while playing accompanying music straight from the device, so that everyone shares the experience.
For young users who depend on constant, immediate socializing of digital content and entertainment, GALAXY Beam introduces a new way of sharing. It becomes much more than a phone-a handy digital tool, deployable anywhere, which can add visual entertainment to a simple street gathering, set the mood for a small party, or simply turn life’s moments into something personally and immediately sharable. With GALAXY Beam, a birthday or anniversary party can be enlivened in seconds by sharing YouTube or Hulu music videos straight onto a ceiling or door. Likewise, students can collectively share videos or study-work in any dormitory room or student lounge, turning group study into a whole new interactive experience right from a desk table or from the palm of their hands. GALAXY Beam is also ideal for action-packed interactive gaming: Users can upload their own games or choose from over 1,000 games available via Game Hub, Samsung’s dedicated virtual gaming store, then project games to co-players or observers to turn gaming into an unbeatably interactive, shared experience. Additionally, GALAXY Beam is convenient tool for mid-sized business workers. An estate agent can beam images of candidate properties to customers as they tour them; or an architect can display draft concepts or designs to co-workers on the spot at a building site or public location.
Despite featuring a full built-in projector, the GALAXY Beam does not compromise on style or portability, measuring just 12.5mm thick and featuring an elegant, ergonomic design. It runs on Android 2.3 Gingerbread which is powered by an impressive 1.0GHz dual-core processor, ensuring great versatility and a highly responsive user interface. An impressive 8GB of internal memory allows ample multimedia storage without compromises, and a powerful 2000 mAh battery ensures greater display power and content freedom.
The GALAXY Beam is exhibited at Samsung stand (Hall 8), Mobile World Congress 2012. For multimedia content and more detailed information, please visitwww.samsungmobilepress.com.
Note to Editors:
Samsung GALAXY Beam Product Specifications
Network
HSPA 14.4/5.76 Mbps 850/900/1900/2100
EDGE/GPRS 850/900/1800/1900
OS
Android 2.3 (Gingerbread)
Display
4.0″ 480×800 (WVGA) TFT
Processor
1.0GHz Dual-Core Processor
Camera
5MP AF ? 1.3MP / Flash
Video
MPEG4, H.263, H.264, WMV, DivX
Recording/Playback: 720p@30fps
Audio
MP3, AAC, AAC?, eAAC?, WMA0fps
Connectivity
BT 3.0?HS, 802.11 b/g/n 2.4GHz, MicroUSB, USB 2.0, 3.5mm Ear Jack
PC Applications
Samsung Kies 2.0
Memory
6GB RAM ? 8GB Internal Memory, MicroSD slot (up to 32GB)
Dimension
64.2 x 124 x 12.5mm, 145.3 g
Battery
2000 mAh
? All functionality, features, specifications and other product information provided in this document including, but not limited to, the benefits, design, pricing, components, performance, availability, and capabilities of the product are subject to change without notice or obligation.
About Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. is a global leader in semiconductor, telecommunication, digital media and digital convergence technologies with 2011 consolidated sales of US$143.1 billion. Employing approximately 222,000 people in 205 offices across 71 countries, the company operates two separate organizations to coordinate its nine independent business units: Digital Media & Communications, comprising Visual Display, Mobile Communications, Telecommunication Systems, Digital Appliances, IT Solutions, and Digital Imaging; and Device Solutions, consisting of Memory, System LSI and LCD. Recognized for its industry-leading performance across a range of economic, environmental and social criteria, Samsung Electronics was named the world’s most sustainable technology company in the 2011 Dow Jones Sustainability Index. For more information, please visit www.samsung.com.
[/toggle]