Wireless Charging: Everything You Need to Know

This year, at the Mobile World Congress held in Barcelona, we saw that Wirless Charging was one of the most talked about subjects. Many big companies such as Samsung, Microsoft and Motorola have been investing heavily in this technology.
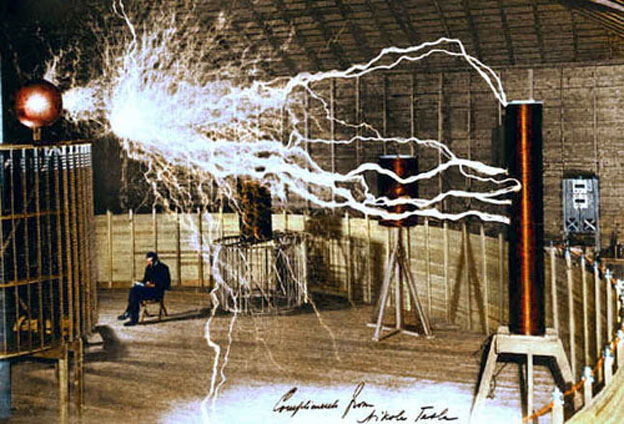
So, what is Wireless Charging? As the name suggests, it is the method of charging a device sans a physical wire. This concept is not new. Nikolas Tesla, whose work in the field of electricity and electromagnetism has defined our modern lifestyle, spectacularly demonstrated the possibility of wireless power transfer in 1891, as visualized by the principle of electromagnetism by Michael Faraday 60 years before. The experiment was quite successful, but long distance wireless charging is still not a practical idea. However, Tesla’s research on short distance wireless power transfer became a reality.
It took nearly a century for the technology to find its way in the mainstream industry, but now, this technology has finally emerged into the consumer electronics market.
In 2008, the newly formed Wireless Power Consortium began outlining plans to design the world without wires, of devices that could juice up upon being dropped on charging pads. But, the journey ahead to seek and work out such technology was difficult. Hence, the work began on achieving this.
How does it work?
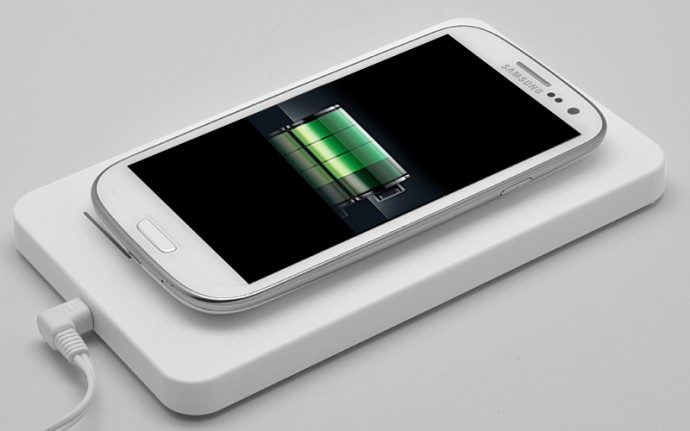
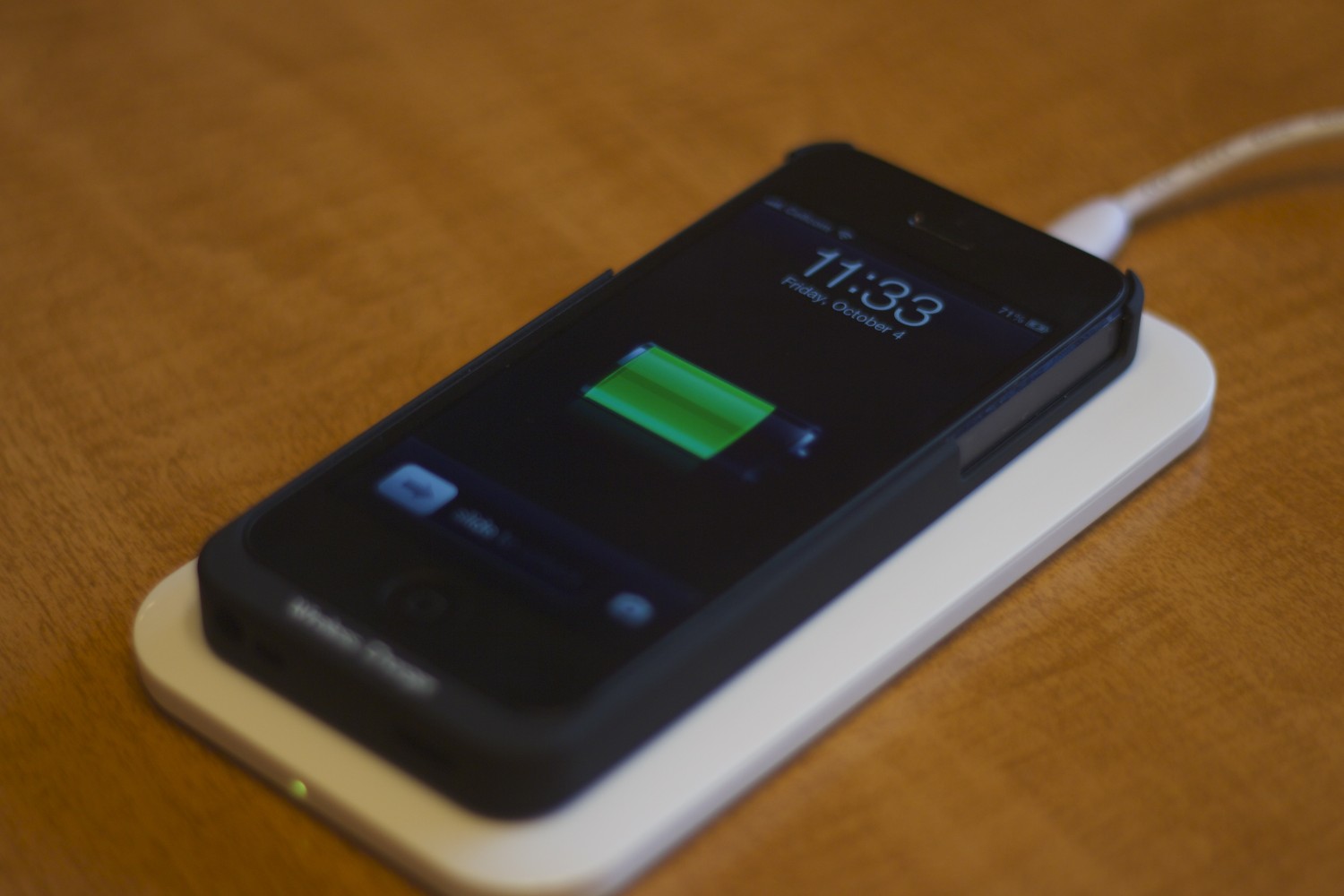
Wireless charging, also known as ‘Inductive Charging’ is based on the principle of magnetic resonance or Inductive Power Transfer- the process where electricity is transferred between two objects through coils. This process uses an induction coil to create an alternating electromagnetic field from within a charging base station. The second induction coil inside the portable device (namely, smartphones) receives the power from the electromagnetic field and converts it into electricity to charge the battery. The two induction coils are in close range to form an electrical transformer.
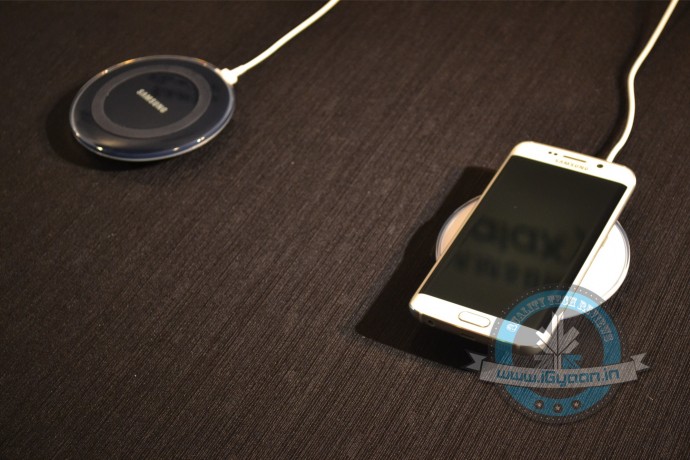
This interface was developed by the Wireless Power Consortium for inductive electrical power transfer over 4cm. You just have to place the device on to the power transmission pad, and it charges using resonant inductive coupling. Just plug in the charging dock and place your device on the charging pad. Then, watch your device juice up. It’s that simple. For now, Qi, pronounced as ‘Chee’ is leading in the wireless charging technology.
Asus, HTC, LG, Motorola, Samsung and Huawei are among the few mobile device manufacturers that are working towards the required standard of Qi.
To this end, the industry has set up three groups that are working to standardise wireless charging technologies: the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) and its Qi standard, the Power Matters Alliance (PMA) and the Alliance for Wireless Power (A4WP).
Advantages
- No requirement of a power cord: The first and foremost reason wireless charging is being worked upon is to eliminate the use of wires and cables. Elimination of cables also means less e-wastage.
- Portability: It is small. Hence, you can carry it anywhere along with you. It can be used in your car, house or garden.
- Ease of access: Wireless charging points are slowly being accepted in different outlets and food joints. For example, a type of wireless charger is being used in some McDonald’s outlets in UK. This device allows multiple devices to charge at the same time.
- Environmentally friendly: The growing use of wireless charging technologies reduces CO2 emissions by hundreds of tons each year by eliminating disposable batteries and cords. Your use of a wireless charging device will be contributing to a more sustainable environment by helping to reduce world waste.
- Safety: Wireless charging eliminates sparks and debris related to wired contacts.
For now, there are two very important factors that may play foul against wireless power charging:
- A risk of radio interference: Emissions from the wireless charger may cause radios and other devices using energy in the same frequency range to malfunction. This is due to the radiation and the signals which cut each other if they are in the same frequency.
- Energy consumption: Wireless chargers will always waste more power than their wired versions, and the more flexible adaptive resonance devices will be most at risk of that.
Standardisation would allow the ecosystem for wireless charging to develop and evolve fast. But, it is hard to say about the future of this technology. This technology has just started out and is still in its developing process. But, if it works out successfully on a large scale, people would be able to charge all of their devices wirelessly in restaurants, airports, public spaces, cars and living spaces, freeing them from the burden of carrying their power cords.























 ! For i
! For i