The world’s most popular mobile OS, Android has once again been subjected to a wide scale malicious attack. A security firm “Check Point” discovered a new malware which replace portions of known apps with its own code. Noteworthy, the malware has affected more than 25 milion devices around the globe, out of which 15 million are in India alone.
According to Check Point, the malware is named “Agent Smith” and is designed to target known vulnerabilities of the Android operating system. The application was revealed to partially replace code on legitimate apps with malicious code. Notably, the whole process was exectuted without the knowledge or permission of the device owner.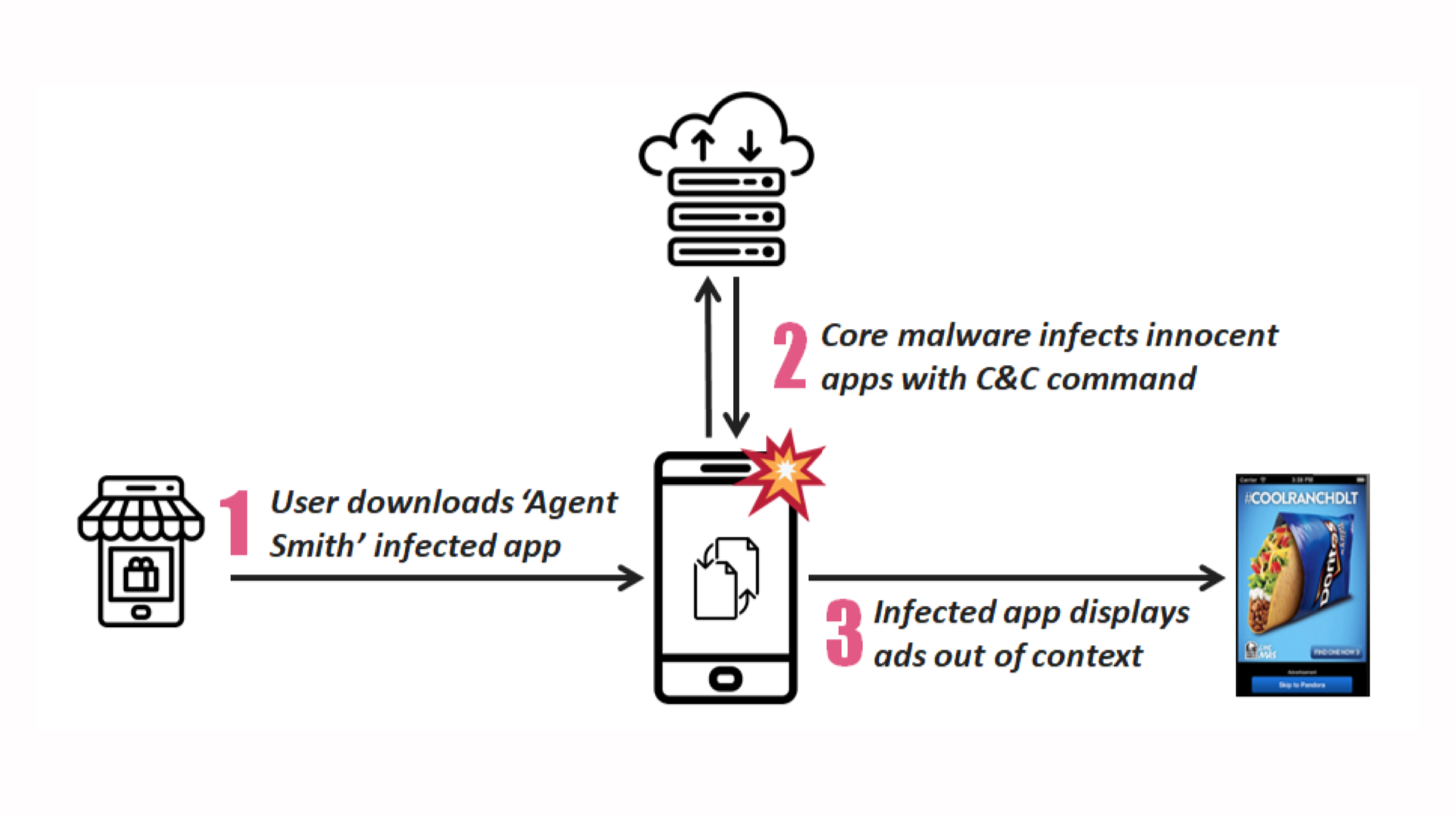
Surprisingly, the malware is not intended to steal user data, instead, it injected the infected apps with lines of code so that they display advertisements. The developer would earn ad credits whenever a user with infected applications would watch or click on the display advertisements. Therfore, the developer could gain monetary value with the whole scheme. 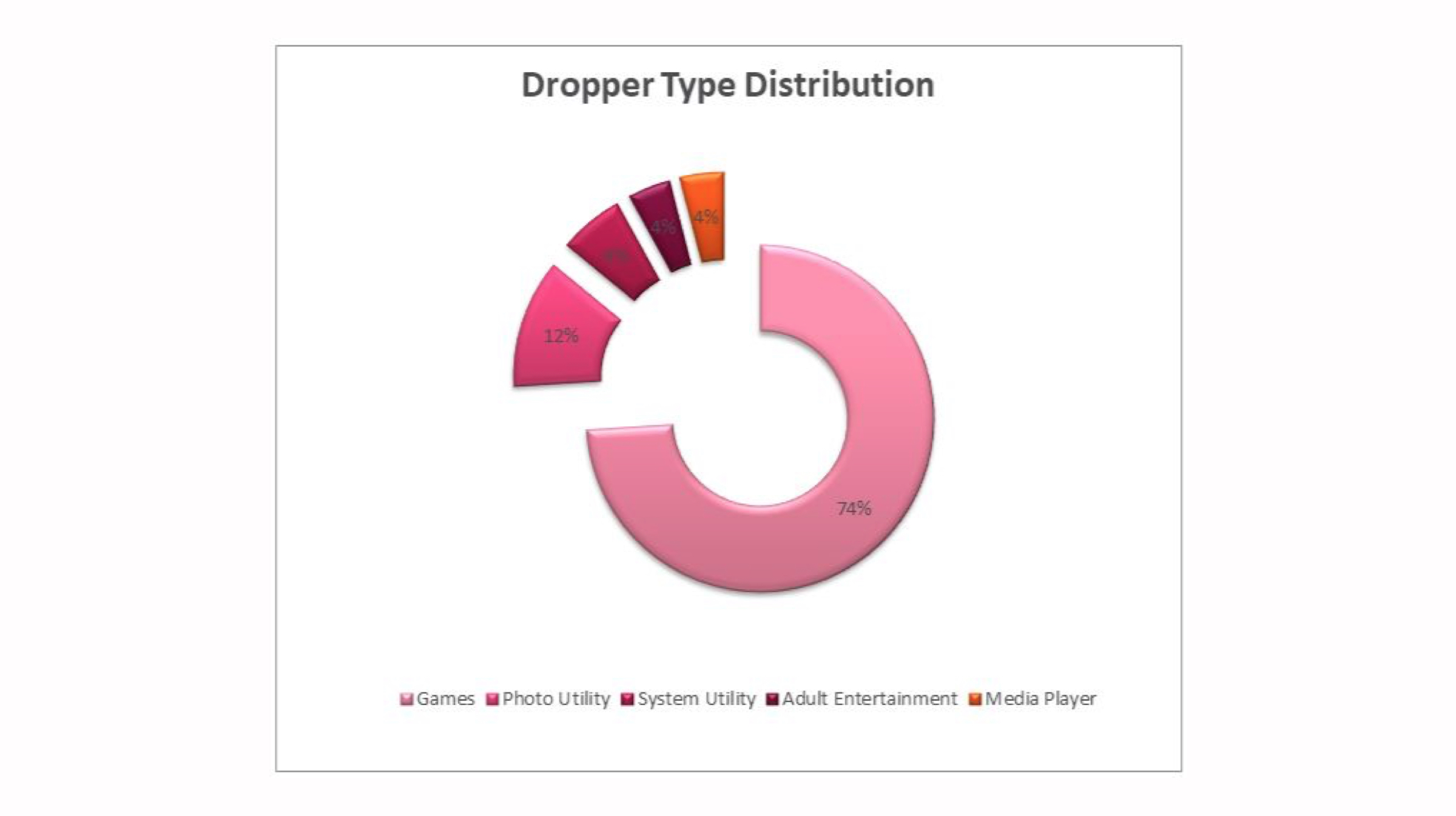
The reserach agency revealed that the Agent Smith malware mainly targeted well-known apps like WhatsApp and Flipkart, therefore, accounting for the astounding reach it had. The source of the malicious app was traced back to a third party application store which is called 9Apps. The malware was concealed in programs like games, video players and adult entertainment apps which have high demand. 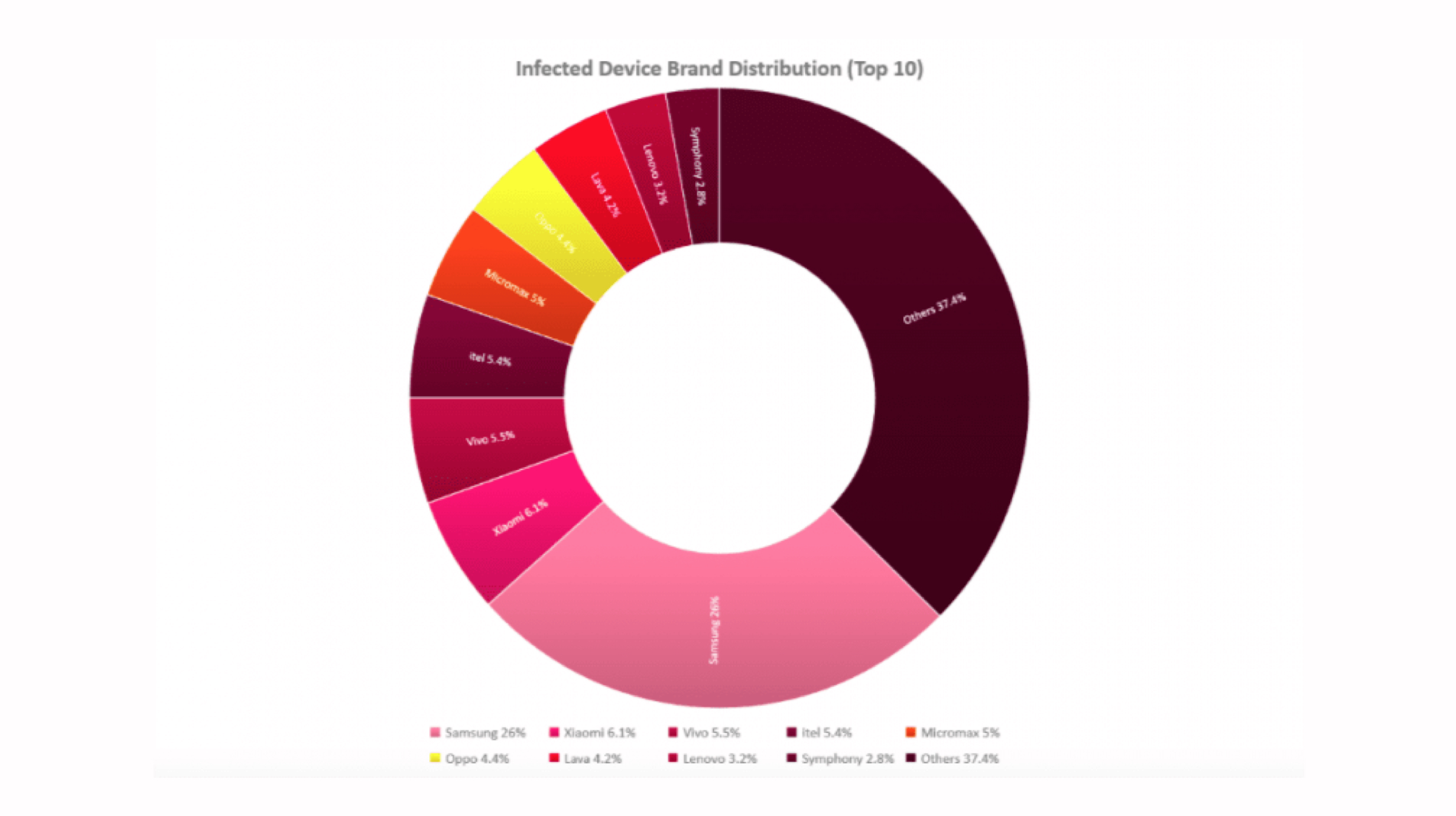
Check Point also shared a donut graph that shows the distribution of malware on smartphones manufactured by OEMs. At over 26 percent, Samsung device owners carry the maximum share in the information representaion tool.
Aside from 15 million Indian smartphones, the malware was even able to spread onto 3,00,000 devices in the US. Surprisingly, the exploits used by the malware to execute the infection process were patched several years ago. However, a large number of developers did not update their respective applications.
Also Read: Apple Will Soon Launch Multiple New iPad Models
This is just one security breach that has made out to the public. It wont be wrong to assume that several other cases like this still remain covered. Conclusively, in this day and era of widespread technology, nothing seems to be truly safe regardless of security measures that are implented.







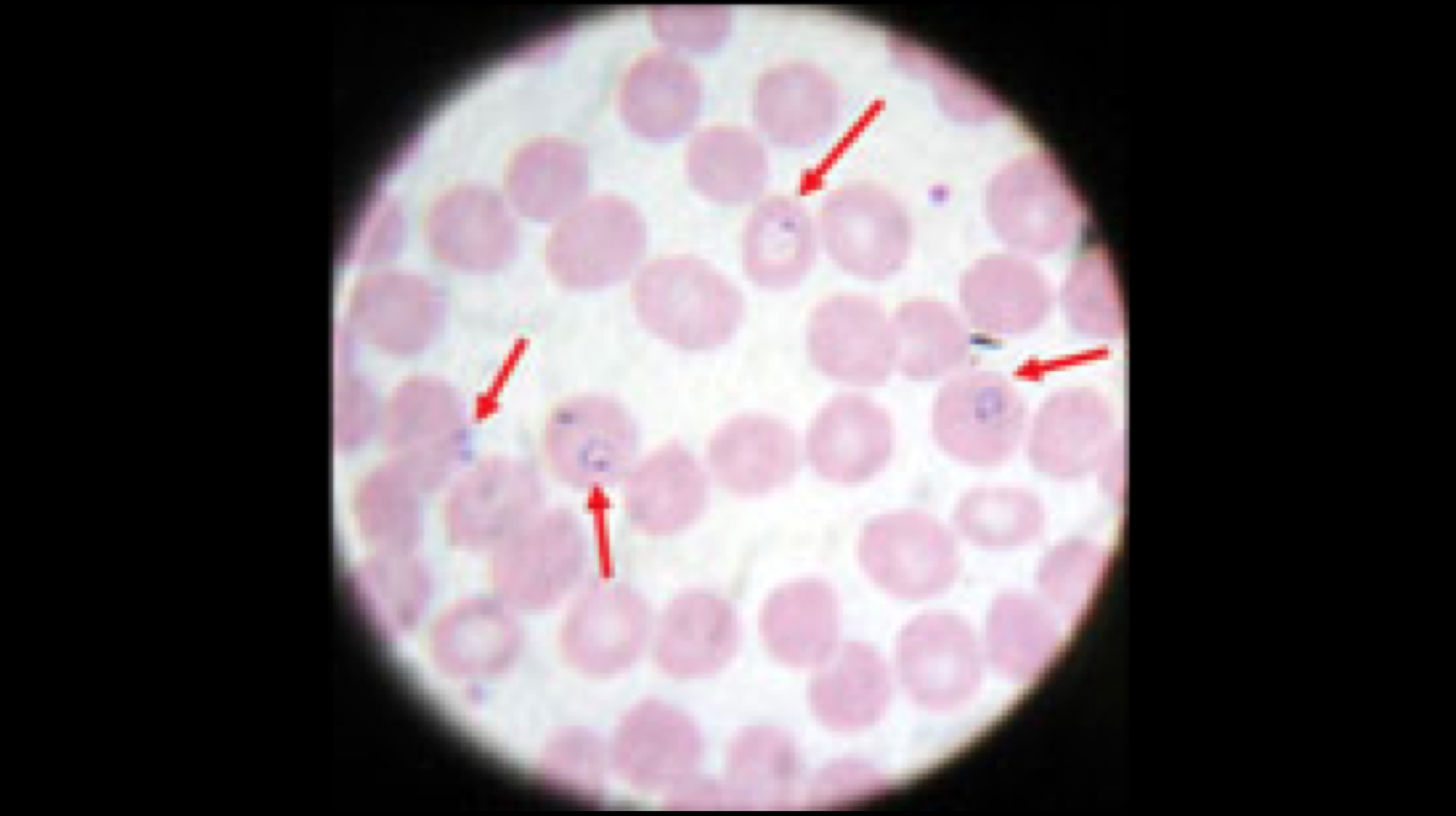

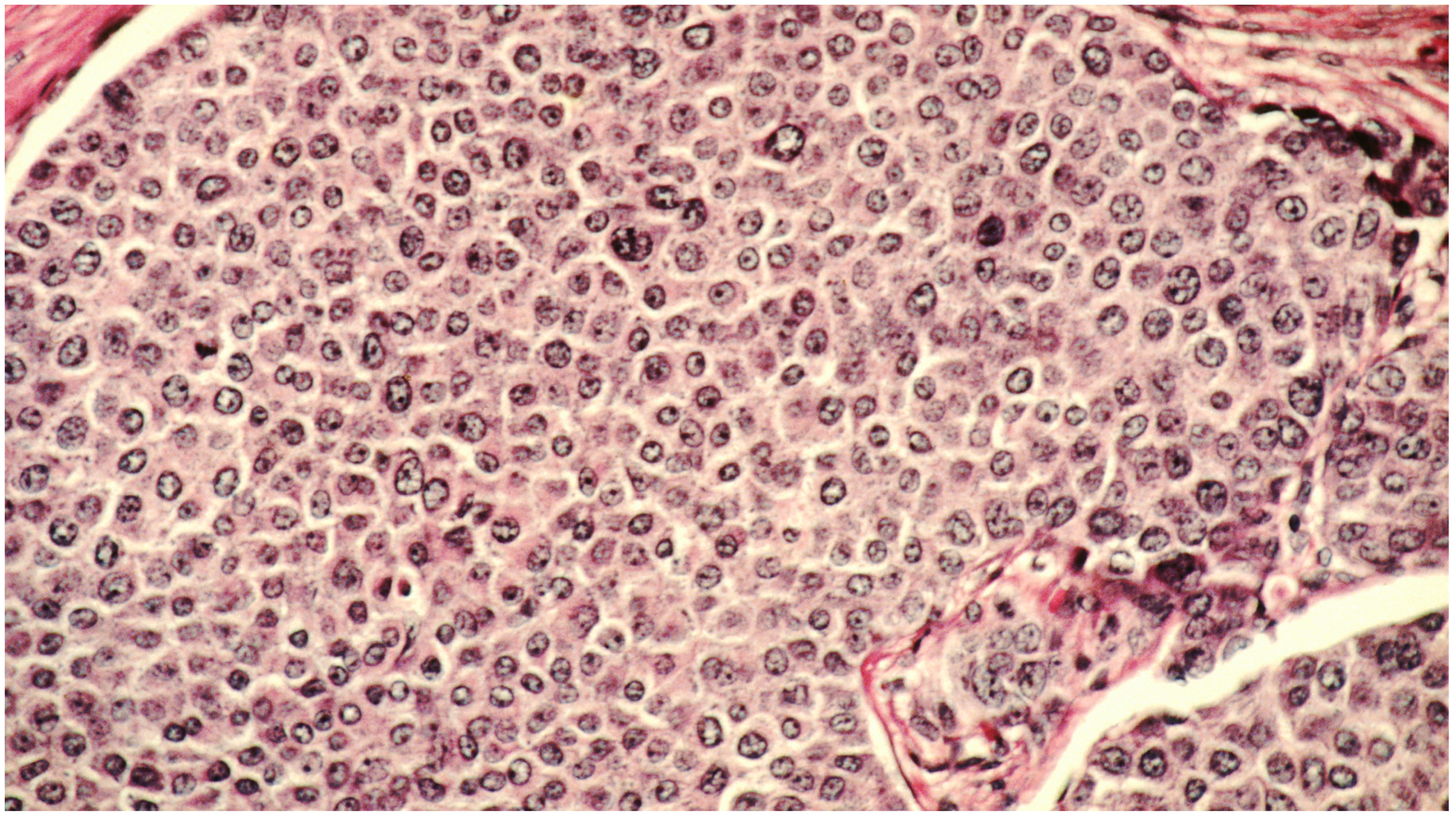
 The test has been patented with the name “Microfluidic Array for the quantification of Cell Invasion”, or MAqCI. The technique makes use of a device to analyze the primary features of metastasis (cancer that has spread to other sites). Reports further state that the MAqCI device was accurate in its predictions regarding breast cancer cell lines and of tumours that were grown in animals.
The test has been patented with the name “Microfluidic Array for the quantification of Cell Invasion”, or MAqCI. The technique makes use of a device to analyze the primary features of metastasis (cancer that has spread to other sites). Reports further state that the MAqCI device was accurate in its predictions regarding breast cancer cell lines and of tumours that were grown in animals. 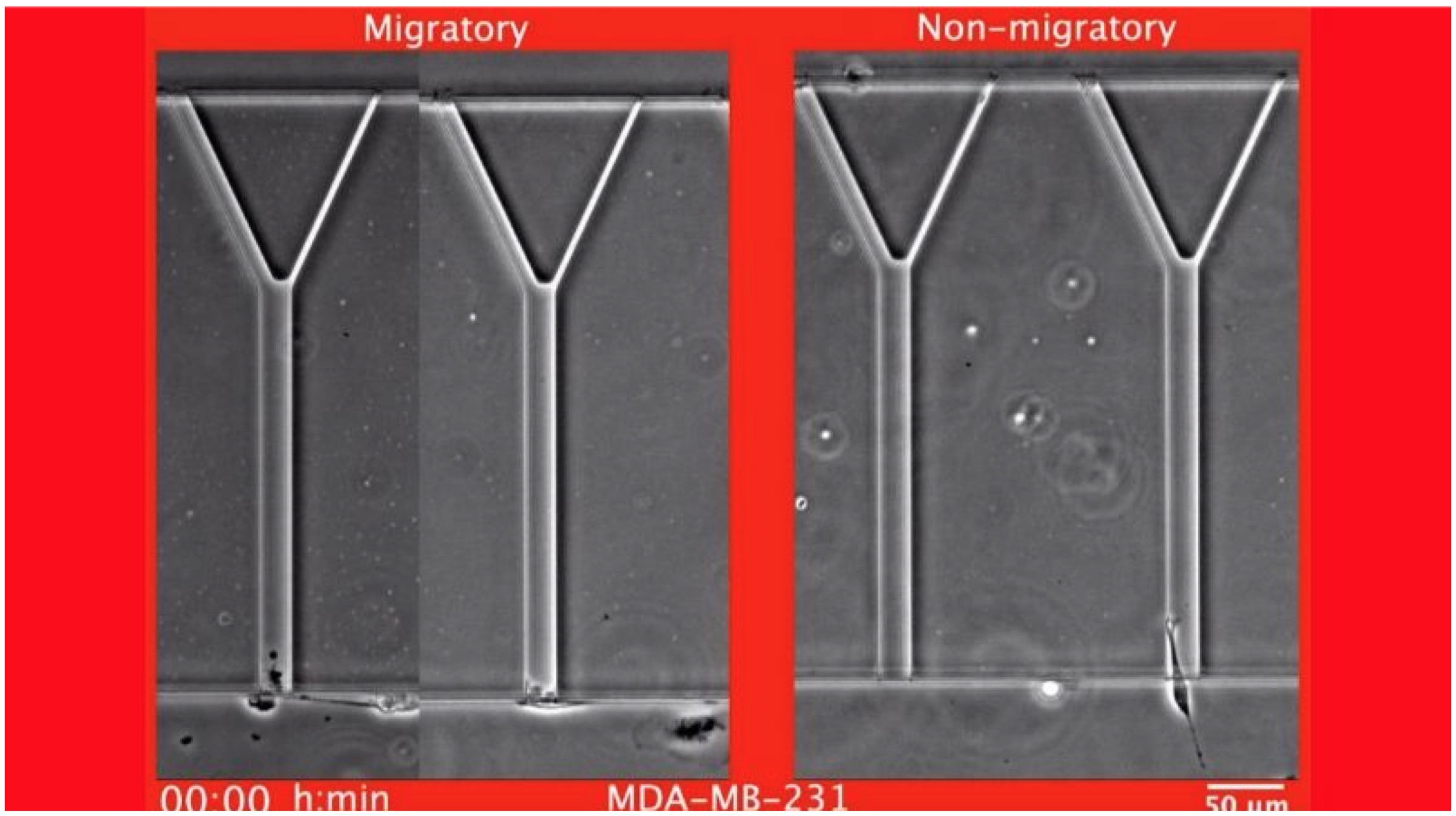 Since a doctor cannot really predict with confidence whether the cancer mass will be aggressive in the future or not, tests like MAqCI become highly necessary to track the movement of the metastasis cancer. The major challenge, however, remains in the case that failure in the prediction of the cancer mass. This is because anonymity of the metastasis can lead to overtreatment in some cases, leading to inadequate treatment methods. The new test will also help clinicians to choose the most compliant and necessary drugs to prevent the spread of malignant cells.
Since a doctor cannot really predict with confidence whether the cancer mass will be aggressive in the future or not, tests like MAqCI become highly necessary to track the movement of the metastasis cancer. The major challenge, however, remains in the case that failure in the prediction of the cancer mass. This is because anonymity of the metastasis can lead to overtreatment in some cases, leading to inadequate treatment methods. The new test will also help clinicians to choose the most compliant and necessary drugs to prevent the spread of malignant cells. 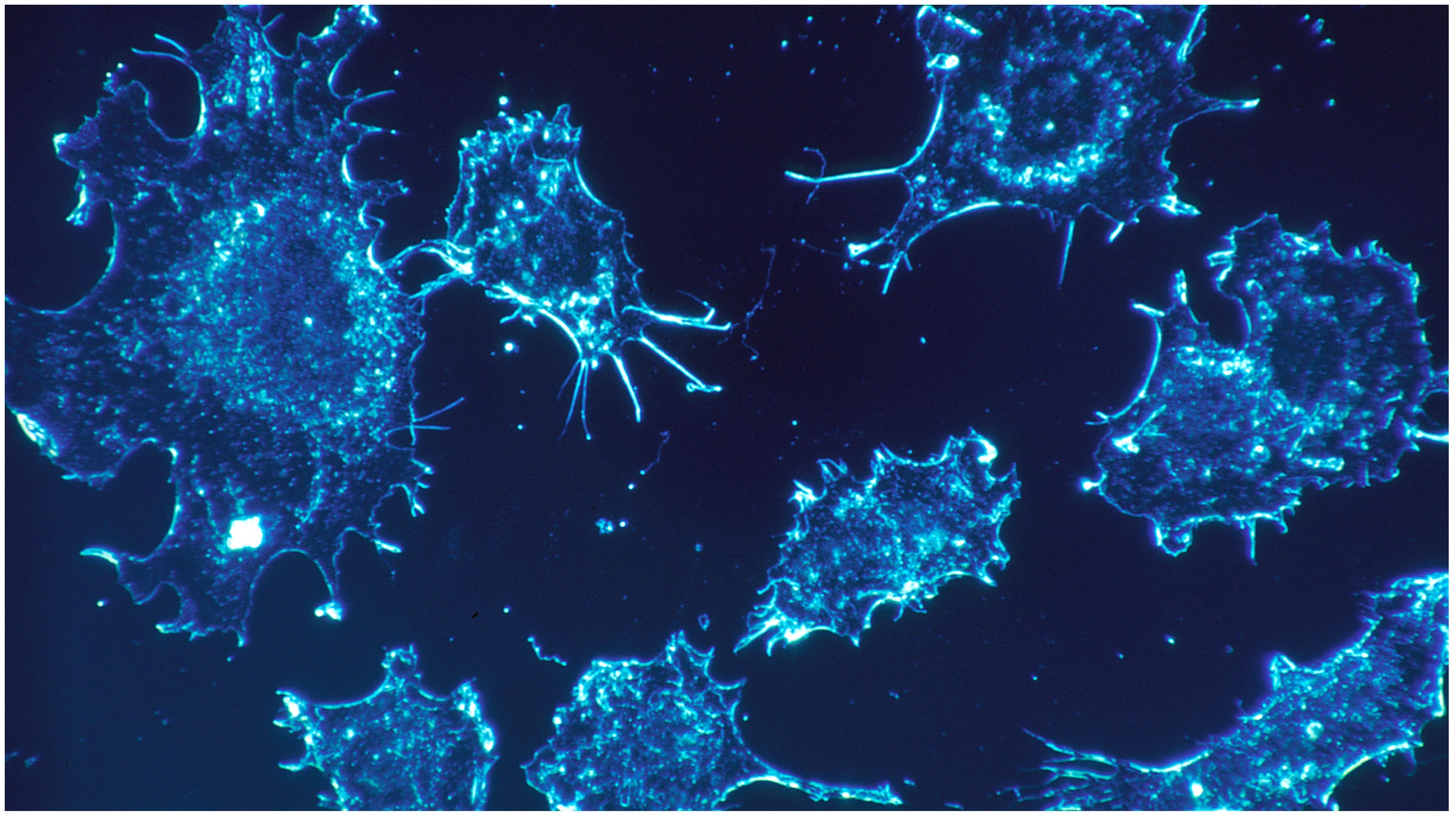
 Researchers from the University of Washington have derived inspiration from Origami techniques and have developed a solution that can serve to keep spacecrafts safe from collisions. They are designing materials that can withstand huge amounts of forces and pressure in space. The paper model of the “demo” material implements the incorporation of “folding creases” that forms a basis of Origami models, which in turn cushions the impact forces consequently reducing the chance of material rupture.
Researchers from the University of Washington have derived inspiration from Origami techniques and have developed a solution that can serve to keep spacecrafts safe from collisions. They are designing materials that can withstand huge amounts of forces and pressure in space. The paper model of the “demo” material implements the incorporation of “folding creases” that forms a basis of Origami models, which in turn cushions the impact forces consequently reducing the chance of material rupture.  Also Read:
Also Read: 






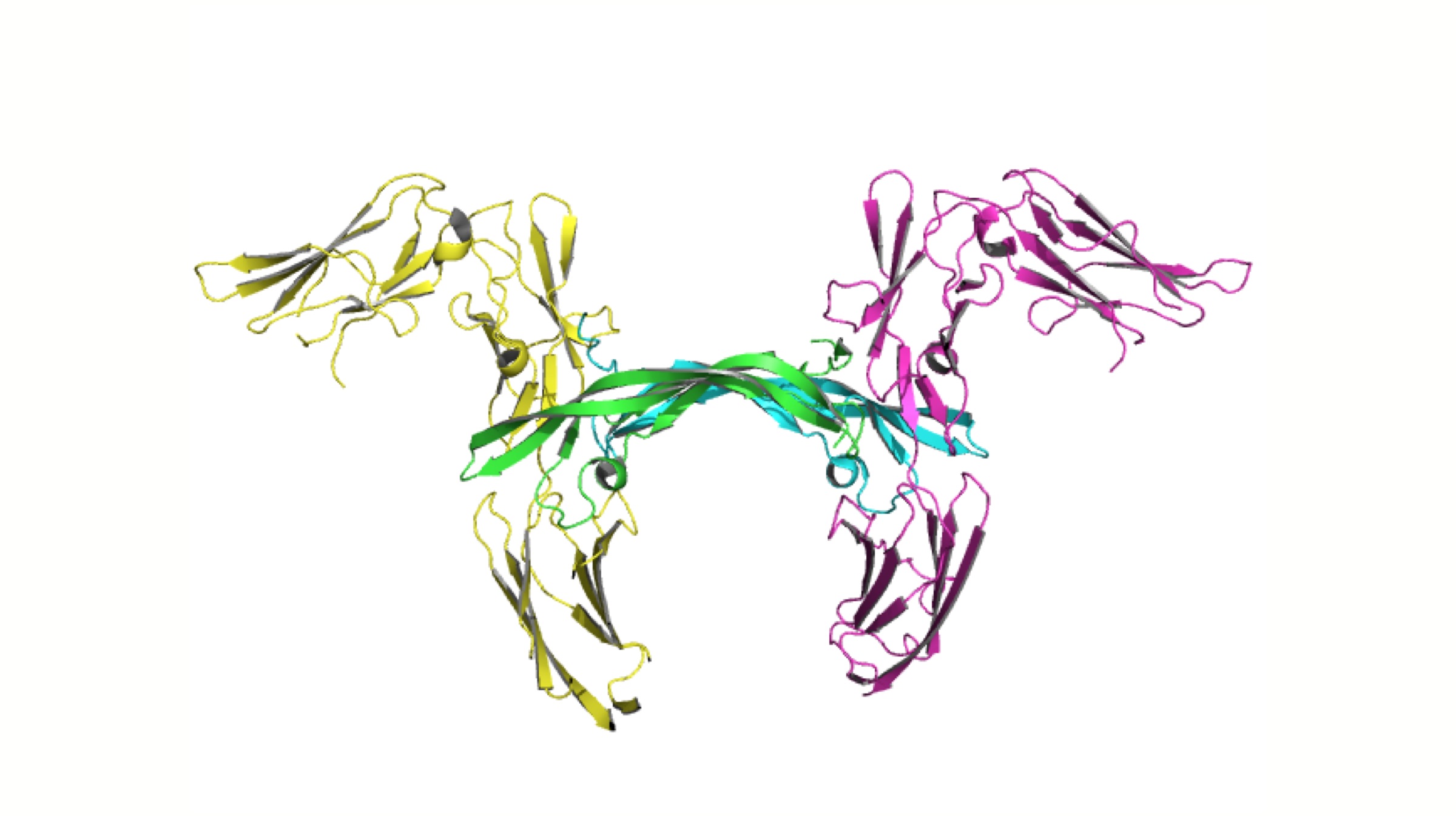 Scientists from the University of Sussex worked in a collaboration with researchers from the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, USA. The treatment involves the usage of ‘Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors’; which is a class of drug currently being used to treat cancer. A number of complex DNA sequencing techniques were implemented, and a new genetic basis of a brain aneurysm form was identified. Manuel Ferreira states that the mutations in the aforementioned gene were completely different from the ones that were previously detected in brain aneurysms.
Scientists from the University of Sussex worked in a collaboration with researchers from the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, USA. The treatment involves the usage of ‘Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors’; which is a class of drug currently being used to treat cancer. A number of complex DNA sequencing techniques were implemented, and a new genetic basis of a brain aneurysm form was identified. Manuel Ferreira states that the mutations in the aforementioned gene were completely different from the ones that were previously detected in brain aneurysms.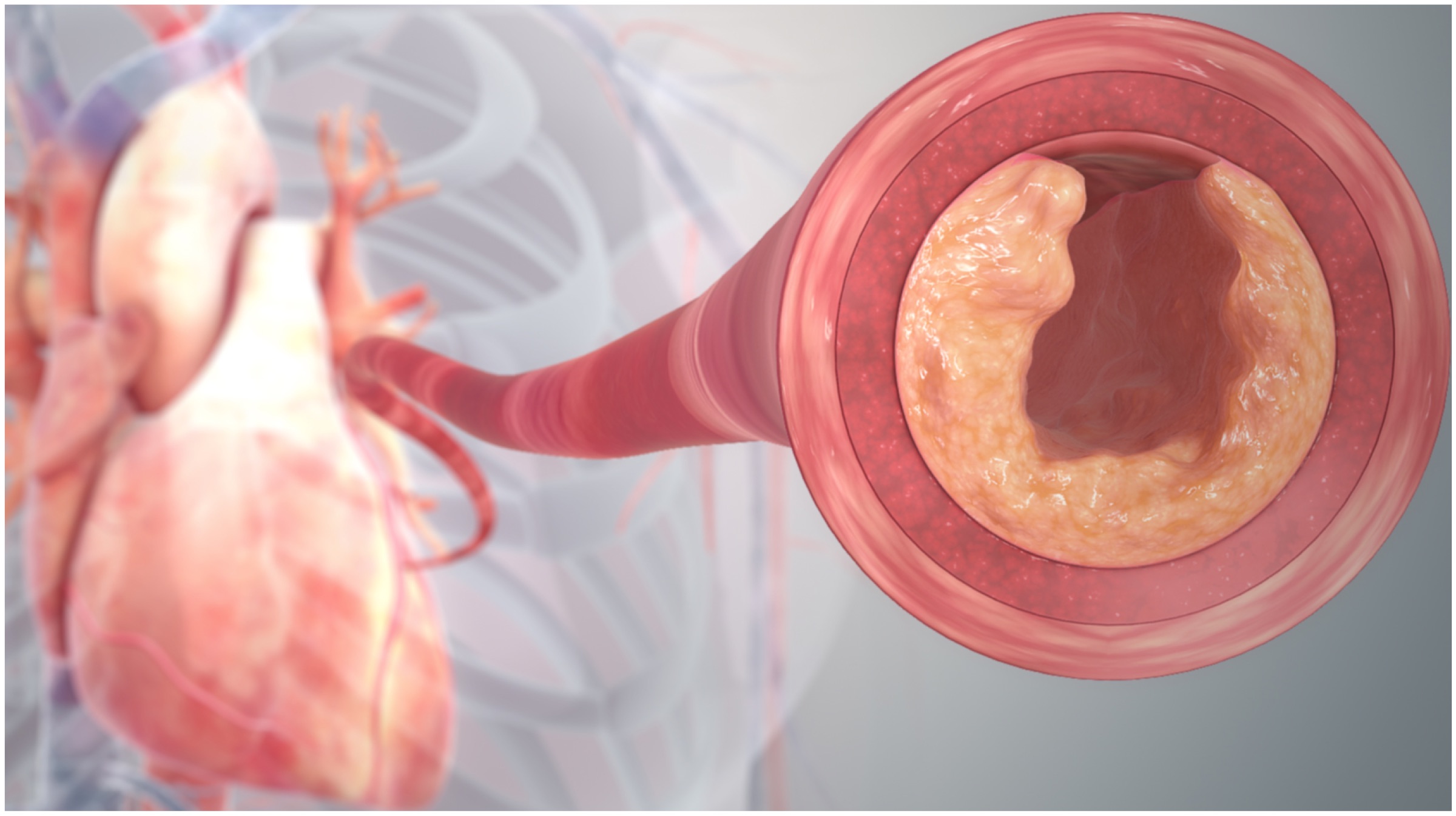 Also Read:
Also Read: 
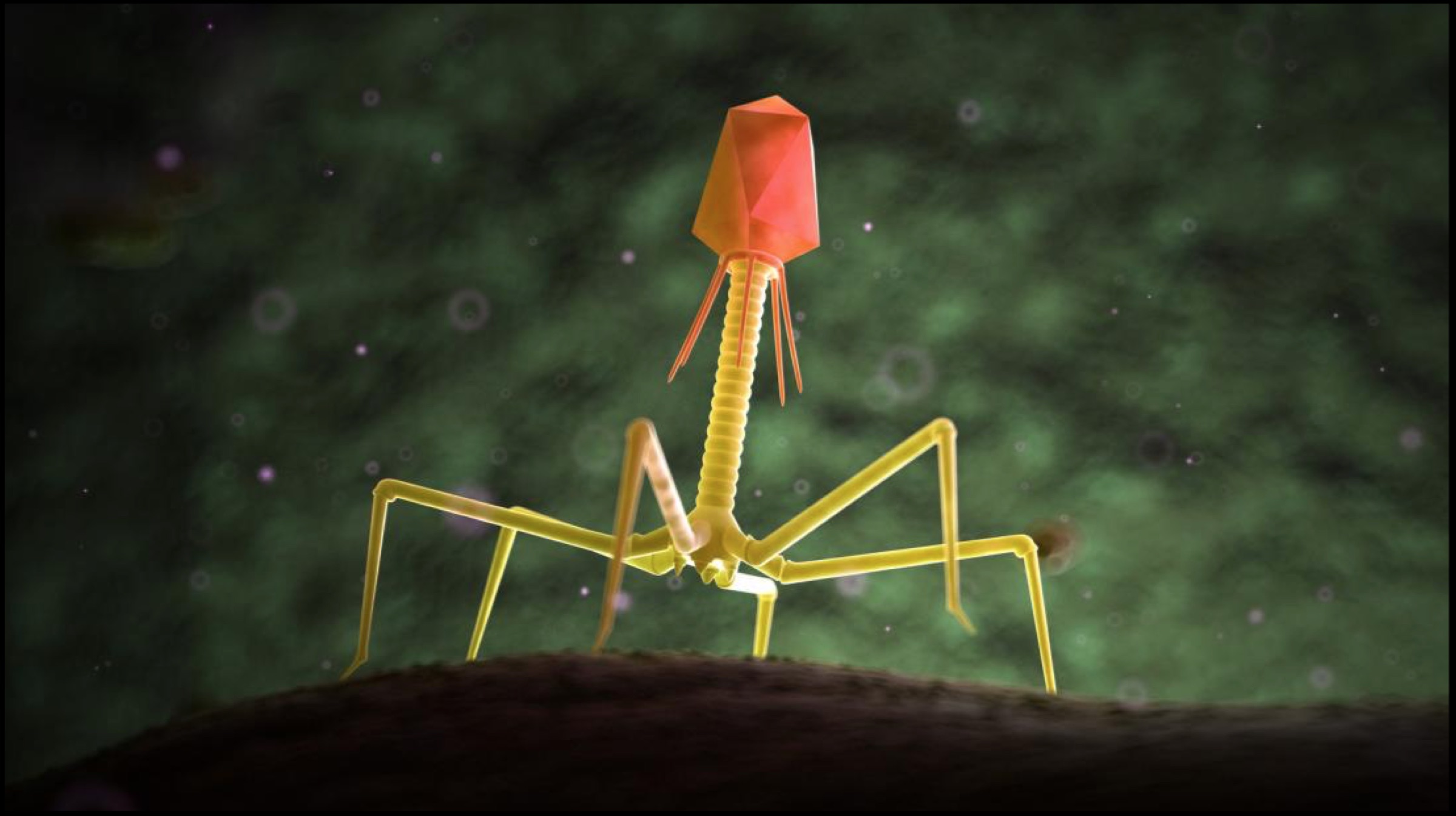

 Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania and Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) in Chevy Chase have put forward evidence that suggests that a category of viruses known as “bacteriophages” can be the solution to antibiotic-resistant bacteria. These bacteria-eating viruses target and kill a variety of strains of bacteria that cause infection. An interesting fact to note is that there are an estimated 1031 bacteriophages on this planet, and different phages target different bacterial strains.
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh in Pennsylvania and Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) in Chevy Chase have put forward evidence that suggests that a category of viruses known as “bacteriophages” can be the solution to antibiotic-resistant bacteria. These bacteria-eating viruses target and kill a variety of strains of bacteria that cause infection. An interesting fact to note is that there are an estimated 1031 bacteriophages on this planet, and different phages target different bacterial strains.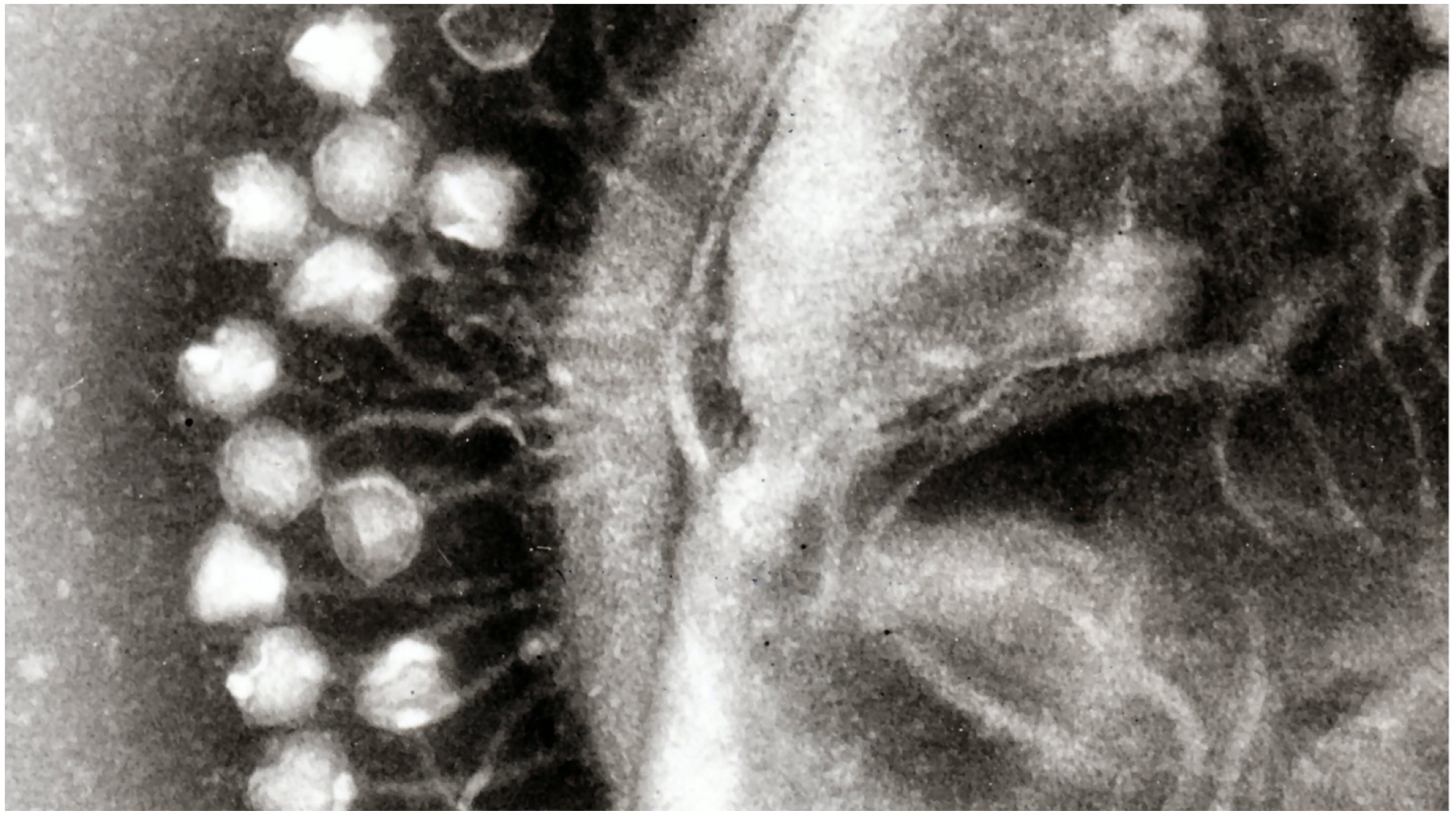 Using bacteriophages (or simply phages) to ward off infections is not a new idea at all. In fact, researchers from Britain, France and Russia were involved in similar investigations since the beginning of the 20th Century, which are proving to be fruitful just now owing to the advancements in research techniques. The “bacteria-attacking” technique was implemented in 2017, where a team of scientists lead by Professor Hatfull achieved a feat nothing short of a miracle.
Using bacteriophages (or simply phages) to ward off infections is not a new idea at all. In fact, researchers from Britain, France and Russia were involved in similar investigations since the beginning of the 20th Century, which are proving to be fruitful just now owing to the advancements in research techniques. The “bacteria-attacking” technique was implemented in 2017, where a team of scientists lead by Professor Hatfull achieved a feat nothing short of a miracle.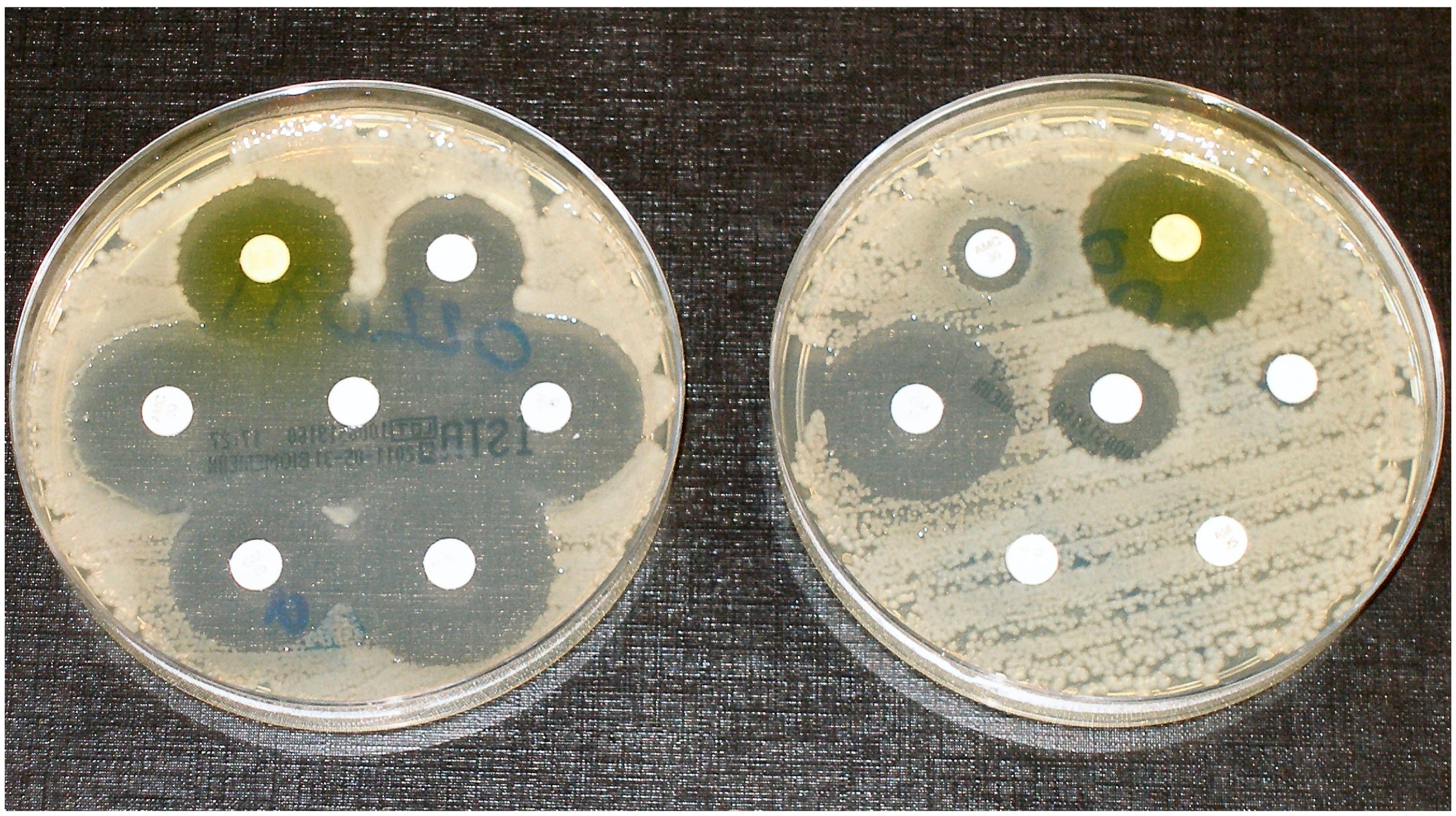 The team of scientists were able to treat an infection experienced by a 15-year-old patient with the help of carefully chosen phages. The patient suffered from cystic fibrosis, which increased the risk of infections because of a buildup of thick mucus in the lungs (and other organs). Moreover, the genetic condition is virtually incurable. After a double lung transplant, it was detected that the patient’s surgery wound was reddened because of a liver infection. Another patient with a similar condition also developed an infection after his surgery. When the infections showed signs of resistance to antibiotics, the scientists decided to use bacteriophages to kill the concerned bacteria.
The team of scientists were able to treat an infection experienced by a 15-year-old patient with the help of carefully chosen phages. The patient suffered from cystic fibrosis, which increased the risk of infections because of a buildup of thick mucus in the lungs (and other organs). Moreover, the genetic condition is virtually incurable. After a double lung transplant, it was detected that the patient’s surgery wound was reddened because of a liver infection. Another patient with a similar condition also developed an infection after his surgery. When the infections showed signs of resistance to antibiotics, the scientists decided to use bacteriophages to kill the concerned bacteria.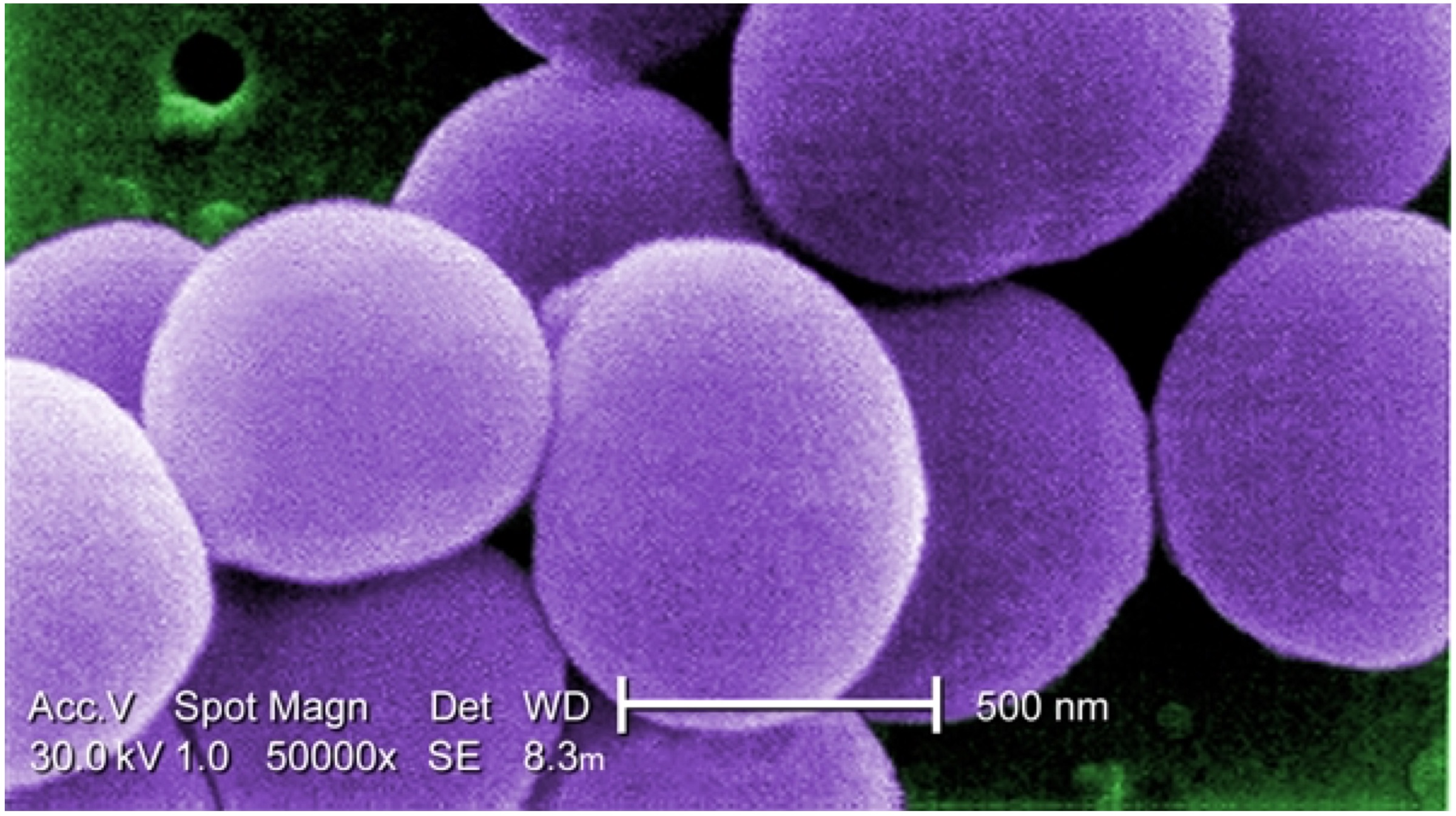 Also Read:
Also Read: 

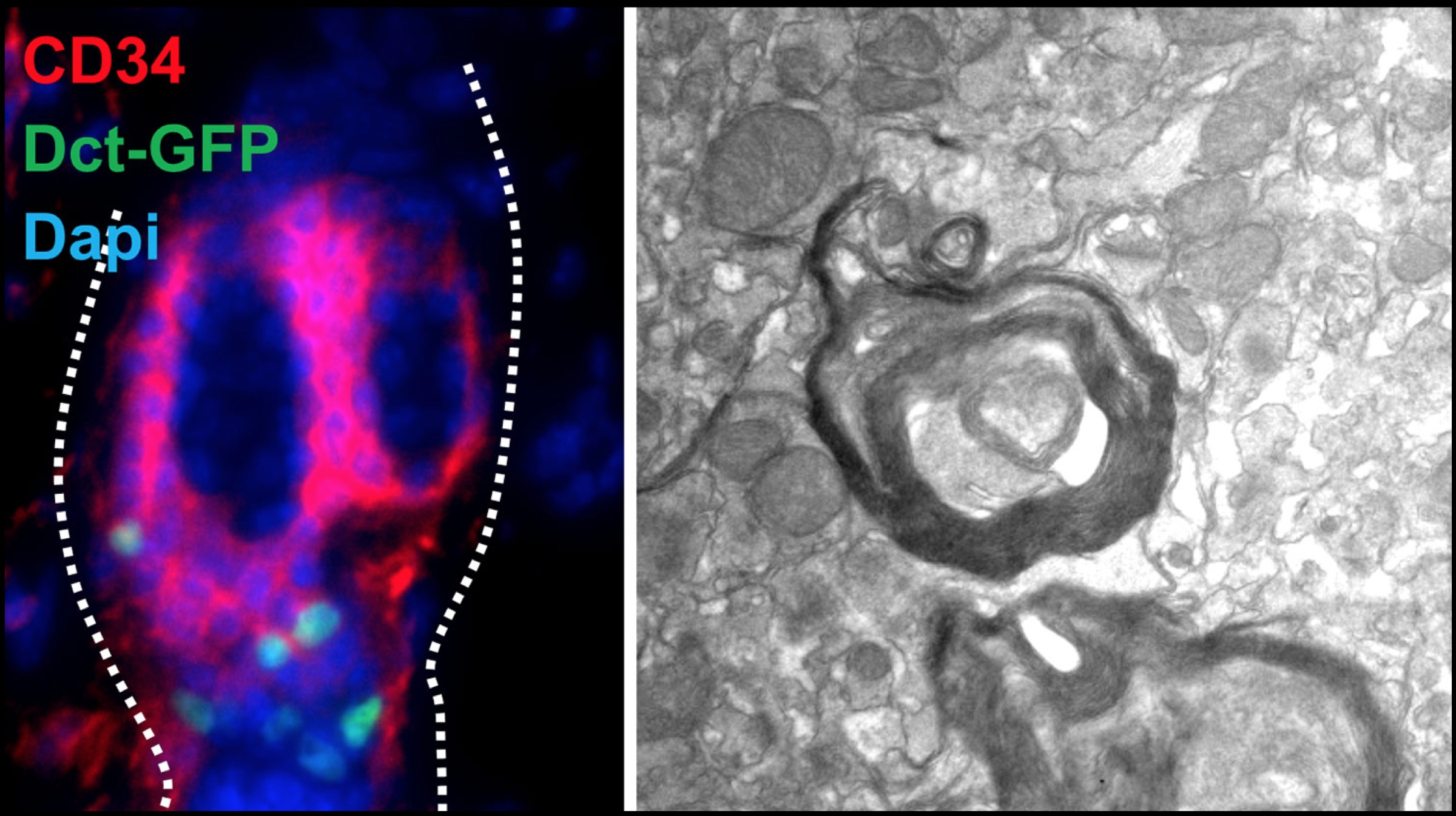
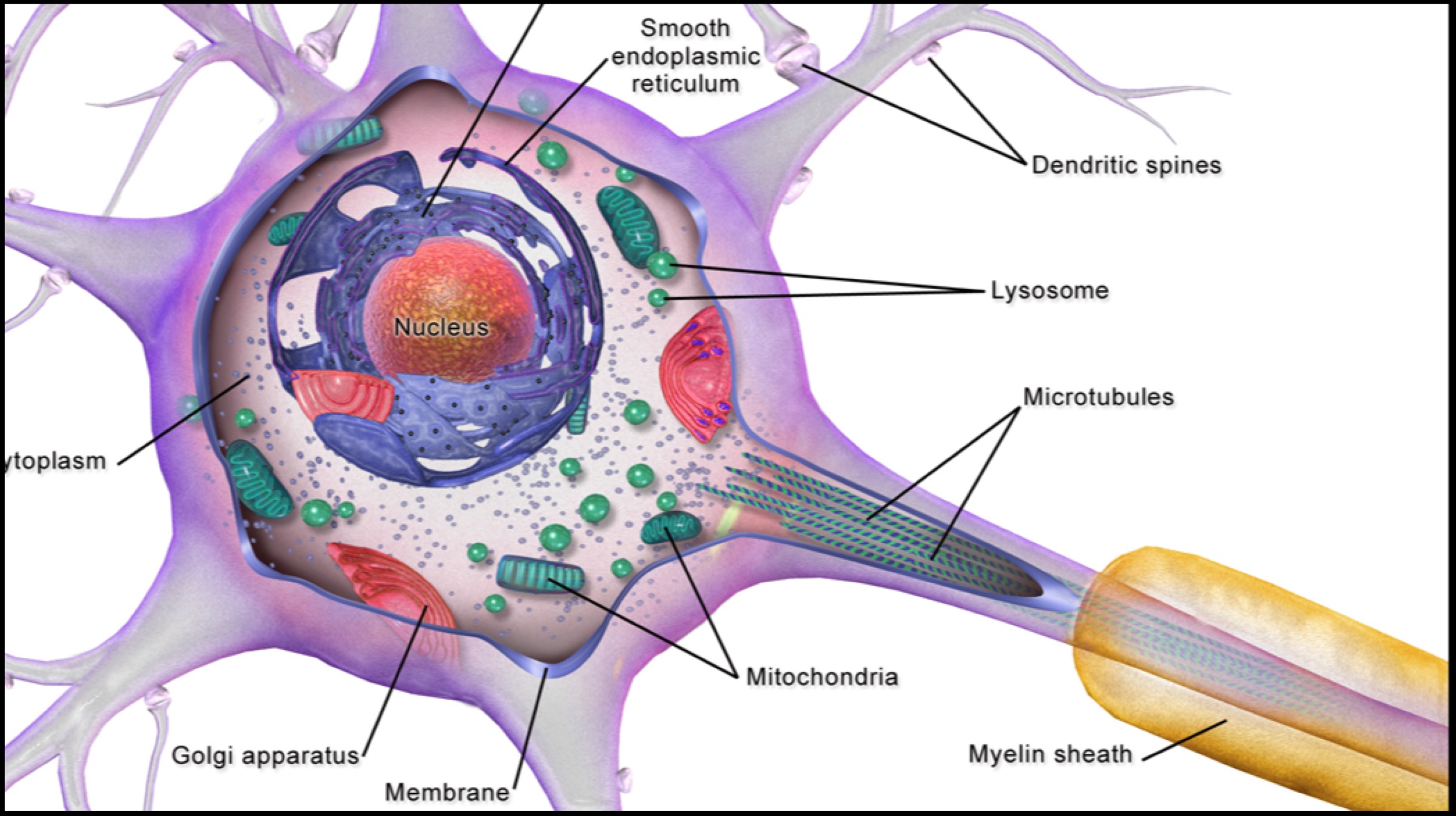 Research performed on mice yielded positive results. Restoration of myelin sheaths in mice led them to believe that stem cells could be a much simpler alternative to using embryonic stem cells. Since the human skin stem cells can be isolated, expanded and used therapeutically, they can possibly improve the chances of functional recovery in case of any injury to the neurons in the nervous system. Dr Thomas J. Hornyak, the lead investigator in the research plans to expand research into the aforementioned area using collected data.
Research performed on mice yielded positive results. Restoration of myelin sheaths in mice led them to believe that stem cells could be a much simpler alternative to using embryonic stem cells. Since the human skin stem cells can be isolated, expanded and used therapeutically, they can possibly improve the chances of functional recovery in case of any injury to the neurons in the nervous system. Dr Thomas J. Hornyak, the lead investigator in the research plans to expand research into the aforementioned area using collected data. 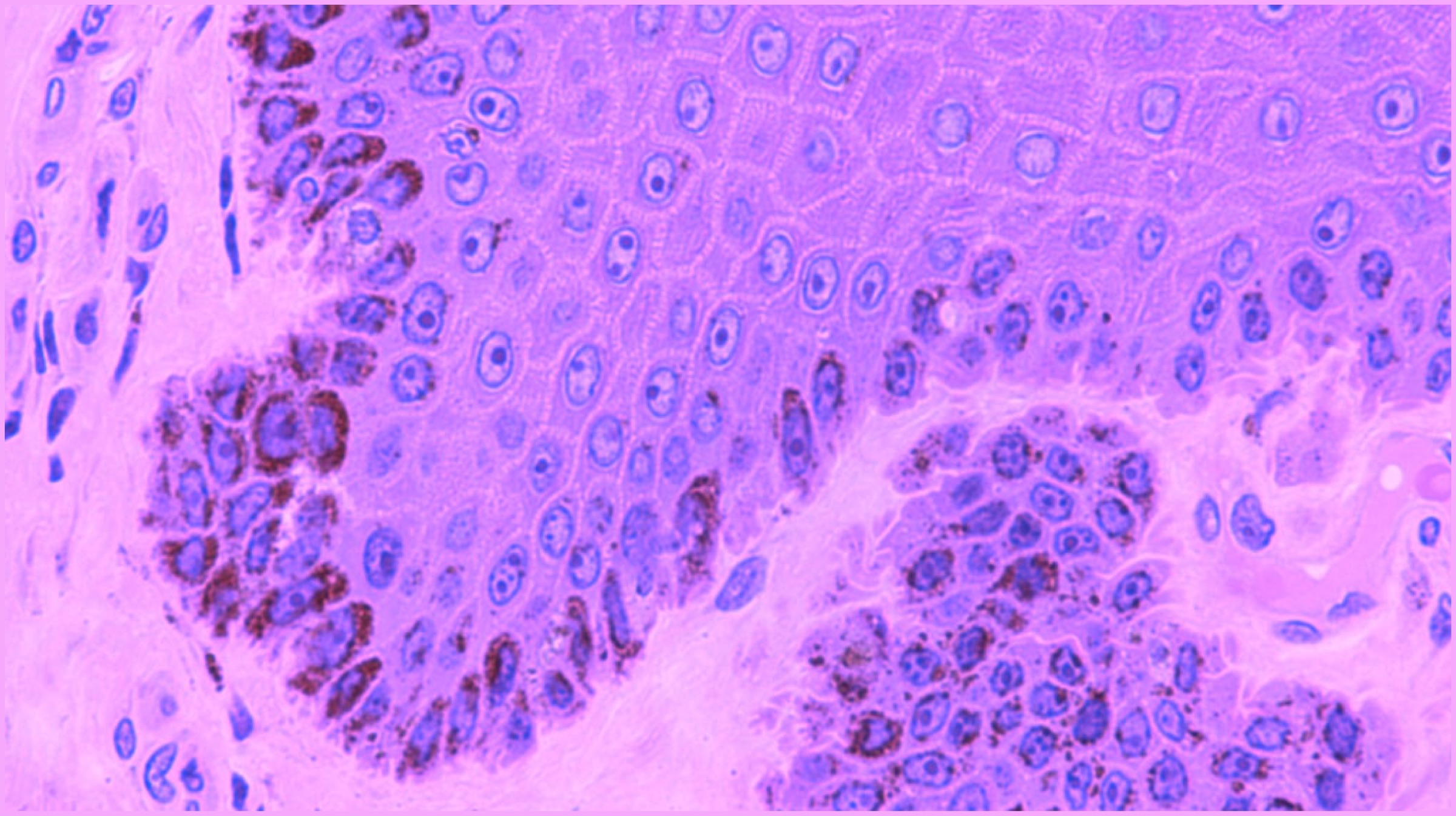 Dr Hornyak and his team of researchers implemented a mouse model to identify a specific version of the melanocyte stem cell. As the name suggests, the cells produce melanin (the pigment that determines the colour of skin and hair) and are present in the hair follicles and skin. These cells have a very unique ability – they can divide limitlessly. In fact, this ability is so unique that it is not present in any other cell in the human body. These stem cells can further develop different types of cells, which depends entirely upon the type of signal provided to them.
Dr Hornyak and his team of researchers implemented a mouse model to identify a specific version of the melanocyte stem cell. As the name suggests, the cells produce melanin (the pigment that determines the colour of skin and hair) and are present in the hair follicles and skin. These cells have a very unique ability – they can divide limitlessly. In fact, this ability is so unique that it is not present in any other cell in the human body. These stem cells can further develop different types of cells, which depends entirely upon the type of signal provided to them. 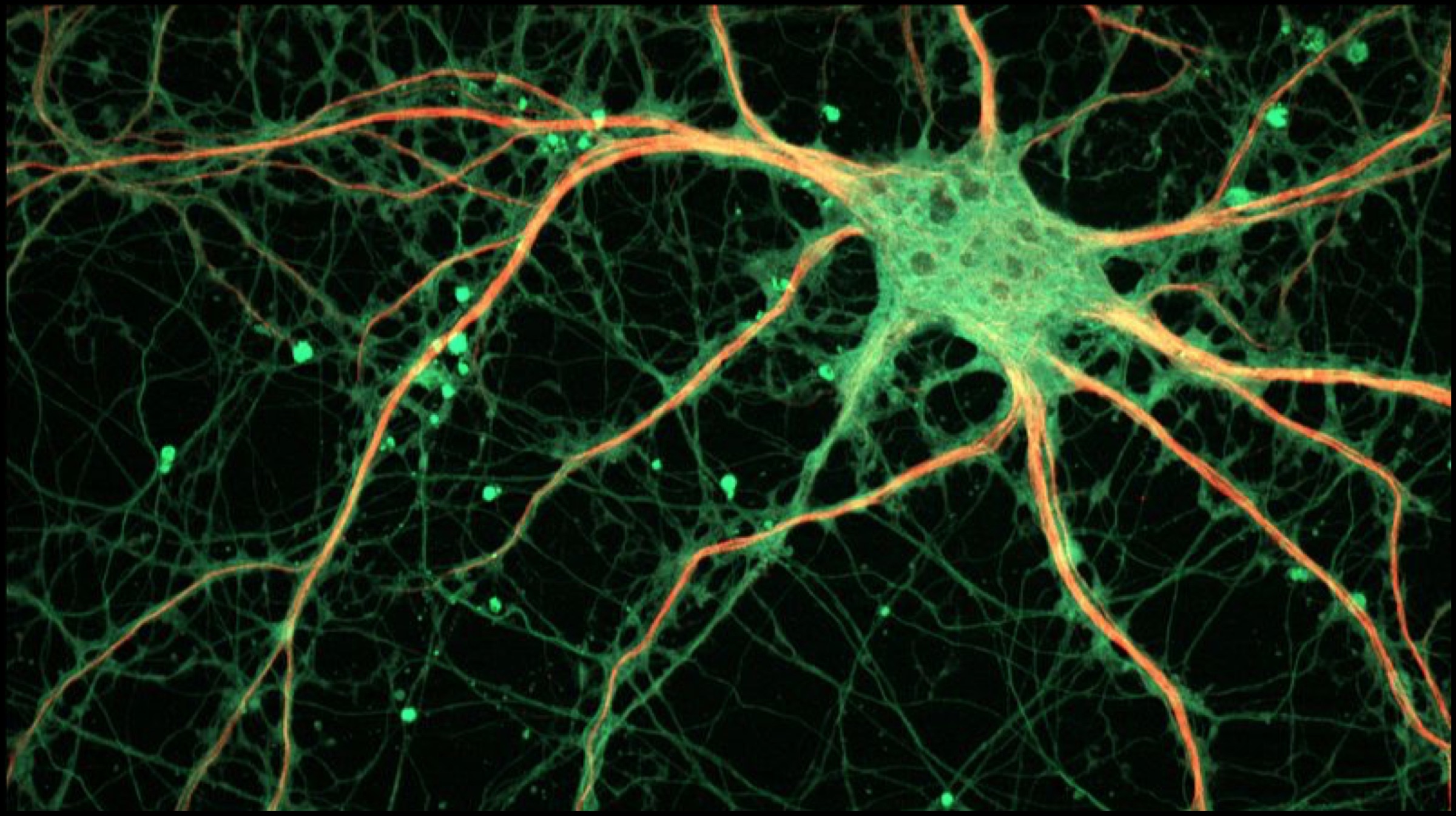 Also Read:
Also Read: 
 Scientists found out that a certain area of the brain behind the ears responded more in case of avid Pokémon fans than those who did not play the game at all. It is already known that humans have specific areas of the brain dedicated to recognizing numbers, words, images and faces. For instance, the human brain responds differently to celebrities like Morgan Freeman, Tom Cruise than it does to other people. Scientists at Stanford decided that to confirm the same study at a younger age, Pokémon fans are the most suited options, as they were already exposed to the game when they were quite young.
Scientists found out that a certain area of the brain behind the ears responded more in case of avid Pokémon fans than those who did not play the game at all. It is already known that humans have specific areas of the brain dedicated to recognizing numbers, words, images and faces. For instance, the human brain responds differently to celebrities like Morgan Freeman, Tom Cruise than it does to other people. Scientists at Stanford decided that to confirm the same study at a younger age, Pokémon fans are the most suited options, as they were already exposed to the game when they were quite young. Also Read:
Also Read: 
